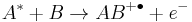Associative ionization
Associative ionization is a gas phase reaction in which two atoms or molecules interact to form a single product ion.[1] One or both of the interacting species may have excess internal energy.
For example
where species A with excess internal energy (indicated by the asterisk) interacts with B to form the ion AB+.
See also
References
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "associative ionization".
References
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "associative ionization".
- Jones DM, Dahler JS (April 1988). "Theory of associative ionization". Physical Review A 37 (8): 2916–2933. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.37.2916. PMID 9900022.
- Cohen, James S. (1976). "Multistate curve-crossing model for scattering: Associative ionization and excitation transfer in helium". Physical Review A 13: 99. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.13.99.